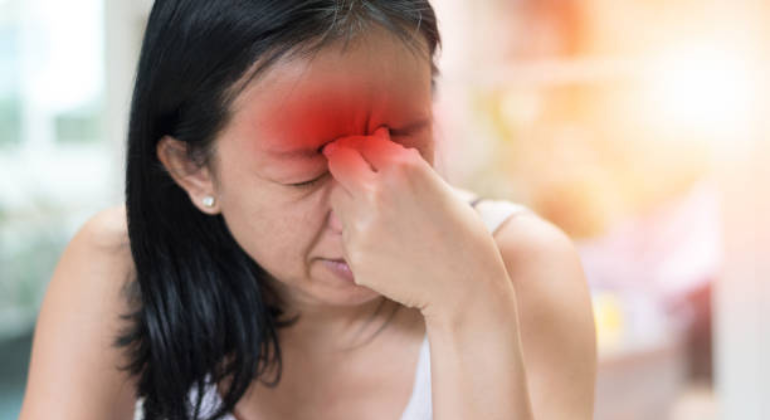
Effective Nerve Pain Relief:
Actions To Take:
- Madication: Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate dosages or take medication provided by doctor.
- Physical therapy can be extremely beneficial in managing nerve pain, especially when caused by nerve compression or injury.